拷贝
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> tmp = {1,2,3};
vector<vector<int>> res;
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.erase(tmp.begin() + 1);
for (auto x: res[0]) {
cout << x << ", ";
}
cout << endl; // 结果为{1,2,3}
return 0;
}
拷贝只对于复合数据结构(如数组,类)才有所不同。尽管不同语言处理细节不同,但简单原则如下:
浅拷贝(Reference)
尽可能拷贝的越少越好,无论是否返回同一个对象,最终的数据源是共享的,一份数据的改变体现在所有的拷贝上。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> A = {1, 2, 3}; // 原始向量
vector<int>& B = A; // 浅拷贝
// 修改 A 的元素
A[0] = 10;
// 输出 B 的元素,B[0] 不会受到 A 的修改影响
cout << "A[0]: " << A[0] << endl; // 输出 10
cout << "B[0]: " << B[0] << endl; // 输出 10
return 0;
}
深拷贝(Constructor)
拷贝所有细节,返回不同的对象,最终的数据源是隔离的,一份数据的改变不会影响其他拷贝。
深拷贝有潜在的诸多问题:
- 拷贝内容过多,通常解决的方案是让开发者自己定义如何拷贝。
- 循环拷贝,属于图的遍历范畴,所以记得去重复。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> A = {1, 2, 3}; // 原始向量
vector<int> B = A; // 深拷贝
// 修改 A 的元素
A[0] = 10;
// 输出 B 的元素,B[0] 不会受到 A 的修改影响
cout << "A[0]: " << A[0] << endl; // 输出 10
cout << "B[0]: " << B[0] << endl; // 输出 1
return 0;
}
数据结构
二元组
与 Python 的 List 非常相似,但 std::tuple 是不可变的数据结构。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
pair<int, string> p = make_pair(12345, "hello!");
cout << p.first << ", " << p.second << endl;
return 0;
}
数组
由于字典的复杂,vector可以代替简单的字典,以下标为key
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 直接使用 vector,不需要 std::vector
v.push_back(6);
for (int num : v) {
cout << num << " "; // 直接使用 cout,不需要 std::cout
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
栈
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> stack;
// 入栈
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
// 出栈
cout << "Popped: " << stack.top() << endl;
stack.pop();
// 栈顶元素
cout << "Top: " << stack.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
队列
也可以使用双端队列 std::deque 来实现队列。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
deque<string> queue = {"Eric", "John", "Michael"};
// 入队列
queue.push_back("Terry");
// 出队列
cout << "Dequeued: " << queue.front() << endl;
queue.pop_front();
return 0;
}
集合
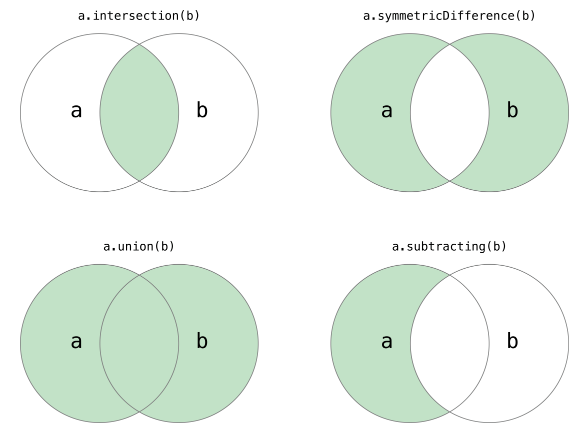
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unordered_set<int> a = {1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2};
unordered_set<int> b = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
// 交集
unordered_set<int> intersection;
for (int num : a) {
if (b.find(num) != b.end()) {
intersection.insert(num);
}
}
// 并集
unordered_set<int> union_set = a;
union_set.insert(b.begin(), b.end());
// 差
unordered_set<int> subtraction;
for (int num : a) {
if (b.find(num) == b.end()) {
subtraction.insert(num);
}
}
// 对称差
unordered_set<int> symmetric_difference;
for (int num : a) {
if (b.find(num) == b.end()) {
symmetric_difference.insert(num);
}
}
for (int num : b) {
if (a.find(num) == a.end()) {
symmetric_difference.insert(num);
}
}
return 0;
}
字典
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unordered_map<string, int> d = { {"sape", 4139}, {"guido", 4127}, {"jack", 4098} };
// 输出
for (const auto& pair : d) {
cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
堆(大)
优先队列通常使用堆来实现。在 C++ 中默认使用最大堆(max-heap),即堆顶是最大元素。如果需要最小堆(min-heap),可以通过自定义比较器来实现。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue<pair<int, string>> pq;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minHeap1; // 小堆, <类型,容器类型,比较函数>
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, function<bool(int, int)>> minHeap2(
[](int a, int b) { return a > b; } // Lambda 表达式作为比较器
);
// 插入元素 (优先级, 数据)
pq.push(make_pair(1, "task 1"));
pq.push(make_pair(3, "task 3"));
pq.push(make_pair(2, "task 2"));
// 顶部元素
cout << "Top: " << pq.top().second << endl;
// 获取并删除优先级最高的元素
pq.pop();
cout << "New Top: " << pq.top().second << endl;
return 0;
}
红黑树(TBD)
前面的unordered_map和unordered_set使用哈希算法来实现。
map和set使用红黑树实现的,红黑树是一颗近似平衡的二叉查找树
//TBD
循环
Range 循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 反向循环
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
列表循环
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个 vector 并初始化
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 方法 1: 范围-based for 循环
cout << "Using range-based for loop:" << endl;
for (const auto& elem : v) {
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法 2: 使用索引
cout << "Using index-based for loop:" << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法 3: 使用迭代器
cout << "Using iterators:" << endl;
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法 4: 使用 C++11 和 lambda 表达式
cout << "Using lambda expression with for_each:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const int& elem) {
cout << elem << " ";
});
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
集合循环
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建 unordered_set 并初始化
unordered_set<int> s = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 方法 1: 范围-based for 循环
cout << "Using range-based for loop:" << endl;
for (const auto& elem : s) {
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法 2: 使用迭代器
cout << "Using iterators:" << endl;
for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法 3: 使用 C++11 和 lambda 表达式
cout << "Using lambda expression:" << endl;
for_each(s.begin(), s.end(), [](const int& elem) {
cout << elem << " ";
});
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
字典循环
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unordered_map<string, int> umap = { {"sape", 4139}, {"guido", 4127}, {"jack", 4098} };
// 使用范围-based for 循环
cout << "Using range-based for loop:" << endl;
for (const auto& pair : umap) {
cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
// 使用结构化绑定 (C++17)
cout << "Using structured bindings:" << endl;
for (const auto& [key, val] : umap) {
cout << key << ": " << val << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
// 使用迭代器
cout << "Using iterators:" << endl;
for (auto it = umap.begin(); it != umap.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
排序与比较
多元素排序
默认递增排序,如果第一个元素相等,比较第二个,以此类推
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建包含多个二元列表的 vector
vector<vector<int>> list = {
{1, 4},
{1, 2},
{5, 6},
{4, 7}
};
// 使用 sort 和自定义比较函数进行排序
sort(list.begin(), list.end());
// 输出排序后的结果
for (const auto& elem : list) {
cout << "[" << elem[0] << ", " << elem[1] << "]" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Lambda排序
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建包含多个二元列表的 vector
vector<vector<int>> list = {
{1, 4},
{1, 2},
{5, 6},
{4, 7}
};
// 使用 sort 和自定义比较函数进行排序
sort(list.begin(), list.end(), [](vector<int> &a, vector<int>& b) {
return a[1] < b[1];
});
// 输出排序后的结果
for (const auto& elem : list) {
cout << "[" << elem[0] << ", " << elem[1] << "]" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
稳定排序
稳定排序在排序时保持了相等元素的相对顺序
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct Employee {
std::string name;
int age;
// 成员函数重载的 < 运算符
// bool operator<(const Employee& other) const {
// // 按年龄排序,若年龄相同则按名字排序
// if (age != other.age) {
// return age < other.age;
// } else {
// return name < other.name;
// }
// }
// 友元函数重载的 < 运算符
// friend bool operator<(const Employee& a, const Employee& b) {
// // 你可以在这里定义不同的排序规则
// // 例如,仅根据名字排序
// if (a.age != b.age) {
// return a.age < b.age;
// } else {
// return a.name < b.name;
// }
// }
};
bool compareByAge(const Employee& a, const Employee& b) {
return a.age < b.age;
}
struct compareByName {
// C++标准库STL中也有默认的less<T>和greater<T>, 例如:less<int>()
bool operator()(const Employee& a, const Employee& b) {
return a.name < b.name;
}
};
int main() {
std::vector<Employee> employees = {
{"Alice", 30},
{"Bob", 25},
{"Charlie", 30},
{"David", 30}
};
// 首先按年龄排序
std::stable_sort(employees.begin(), employees.end(), compareByAge);
// 再按名字排序,保持相同年龄员工的相对顺序
std::stable_sort(employees.begin(), employees.end(), compareByName());
for (const auto& emp : employees) {
std::cout << emp.name << " (" << emp.age << ")" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
– END –