图
社交网络是图比较常用的切入话题之一,包括N度人脉,单向关注,好友关系
edge(i, j)表示从点i到点j有一条边
树
树是一种特殊的图,图成为树的充要条件是:
- N个点,N-1条边
- 所有点连通
有权重
(0)
/ \
1 / \ 4
/ \
(1) (3)
\ /
2 \ / 3
\ /
(2)
# 邻接矩阵
0 1 2 3
0 [ 0 1 0 4 ]
1 [ 1 0 2 0 ]
2 [ 0 2 0 3 ]
3 [ 4 0 3 0 ]
# 邻接表
{
0: [(1, 1), (3, 4)],
1: [(0, 1), (2, 2)],
2: [(1, 2), (3, 3)],
3: [(2, 3), (0, 4)]
}
# 边列表
[
(0, 1, 1),
(1, 2, 2),
(2, 3, 3),
(3, 0, 4)
]
无权重
(0)
/ \
/ \
/ \
(1) (3)
\ /
\ /
\ /
(2)
# 邻接矩阵
0 1 2 3
0 [ 0 1 0 1 ]
1 [ 1 0 1 0 ]
2 [ 0 1 0 1 ]
3 [ 1 0 1 0 ]
# 邻接表
{
0: [1, 3],
1: [0, 2],
2: [1, 3],
3: [2, 0]
}
# 边列表
[
(0, 1),
(1, 2),
(2, 3),
(3, 0)
]
持久化
内存中的数据结构,类等,通常无法直接用来网络传输,或存储在磁盘上,要通过序列化之后进行
序列化
object_to_string: 将内存中的数据结构,类等转化成字符串(字节组数)的过程
反序列化
string_to_object: 将序列化结果,从新解析成对应数据结构的过程
常见的序列化有xml, json, protobuf, thrift, yaml, plist
设计权衡通常有可读性,压缩率
搜索策略
对于可能有环的图的搜索,一定,一定,一定要去重复,重要的事情说三遍
广度优先BFS
BFS是图的遍历策略,该算法从某一指定节点出发,先搜遍所有的邻居节点,然后再拓展到下一层级,
如下图,以树为例,BFS结果是:
[1]
[2, 3, 4]
[5, 6, 7, 8]
[9, 10, 11, 12]
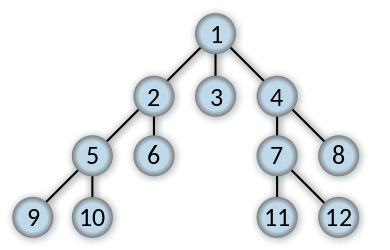
深度优先DFS
DFS图的遍历策略,与BFS策略相反,该算法从某一指定节点出发,先探索尽可能远,然后回溯
回溯是指,先遍历[1, 2, 3, 4], 然后4没有更深的节点,然后把4丢掉,退回[1, 2, 3],再把5填到结果中得到[1, 2, 3, 5],以此类推
如下图:DFS结果是:
[1, 2, 3, 4] pop 4
[1, 2, 3, 5] pop 5, 3
[1, 2, 6] pop 6, 2
[1, 7] pop 7
[1, 8, 9, 10] pop 10
[1, 8, 9, 11] pop 11, 9
[1, 8, 12]
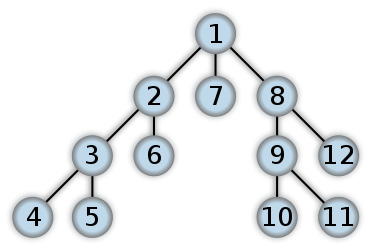
代码实现
图的搜索遍历一定要记得记得去重, 由于树没有环这里省略去重复
递归实现
DFS
def __init__(self):
val = 0
children = []
def search(node):
if node is None:
return
print(node.val)
for sub in node.children:
search(sub)
非递归实现
DFS
nodes_to_visit = [root]
while( len(nodes_to_visit) > 0 ) {
#从尾部取出
node = nodes_to_visit.pop()
print(node.val)
for sub in node.children:
nodes_to_visit.append(sub)
}
BFS
nodes_to_visit = [root]
while( len(nodes_to_visit) > 0 ) {
#从头部取出
node = nodes_to_visit.pop(0)
print(node.val)
for sub in node.children:
nodes_to_visit.append(sub)
}
如果你仔细观察,非递归版本BFS与DFS是非常对称,只是DFS从尾部取出(Stack),BFS从头部取出(Queue)
二分图
把无向图中的节点分成两个阵营A,B。 所有的链接都必须从A阵营连接到B阵营(反之亦然)。这样的图为二分图。
比如异性相亲,2个阵营,每次匹配都只能是异性接触
性质如下:
- 图中不能有奇数环,比如三角形,五边形等
- 可以二分着色,从任意一点着蓝色,连接的节点不能颜色相同,不会有冲突,孤立节点可以分为任意阵营
着色判断法
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def isBipartite(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
n = len(graph)
colored = {}
q = deque()
for i in range(n):
if i not in colored:
colored[i] = 1
q.append(i)
while len(q) > 0:
cur = q.popleft()
for node in graph[cur]:
if node not in colored:
q.append(node)
colored[node] = 2 if colored[cur] == 1 else 1
elif colored[node] == colored[cur]:
return False
return True
拓扑排序
拓扑排序是一种对有向无环图(DAG)进行排序的方法,它对图中的所有节点进行线性排序。
比如课程,先参加A,才能参加B课程。 如果有环,那么A,B循环依赖,无法拓扑排序
课程排序
from collections import defaultdict, deque
class Solution:
def findOrder(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
graph = defaultdict(list)
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for x in prerequisites:
graph[x[1]].append(x[0])
indegree[x[0]] += 1
res = []
q = deque([x for x in range(numCourses) if indegree[x] == 0])
while len(q) > 0:
cur = q.popleft()
res.append(cur)
for node in graph[cur]:
indegree[node] -= 1
if indegree[node] == 0:
q.append(node)
return res if len(res) == numCourses else []
–END–